Alcoholic Liver Disease Treatment Specialist Q&A
Alcoholic liver disease is caused by prolonged, excessive alcohol consumption that damages liver cells and impairs function. Early stages may be silent, but progression can lead to serious complications like cirrhosis. At Digestive Disease Care, our board-certified gastroenterologists provide comprehensive diagnosis and management to support liver health. For more information, contact us today or schedule an appointment online. We have convenient locations to serve you in Babylon NY, East Setauket NY, Forest Hills NY, Jericho NY, Lake Success NY, Melville NY, Mineola NY, Massapequa NY, New Hyde Park NY, and Riverhead NY.
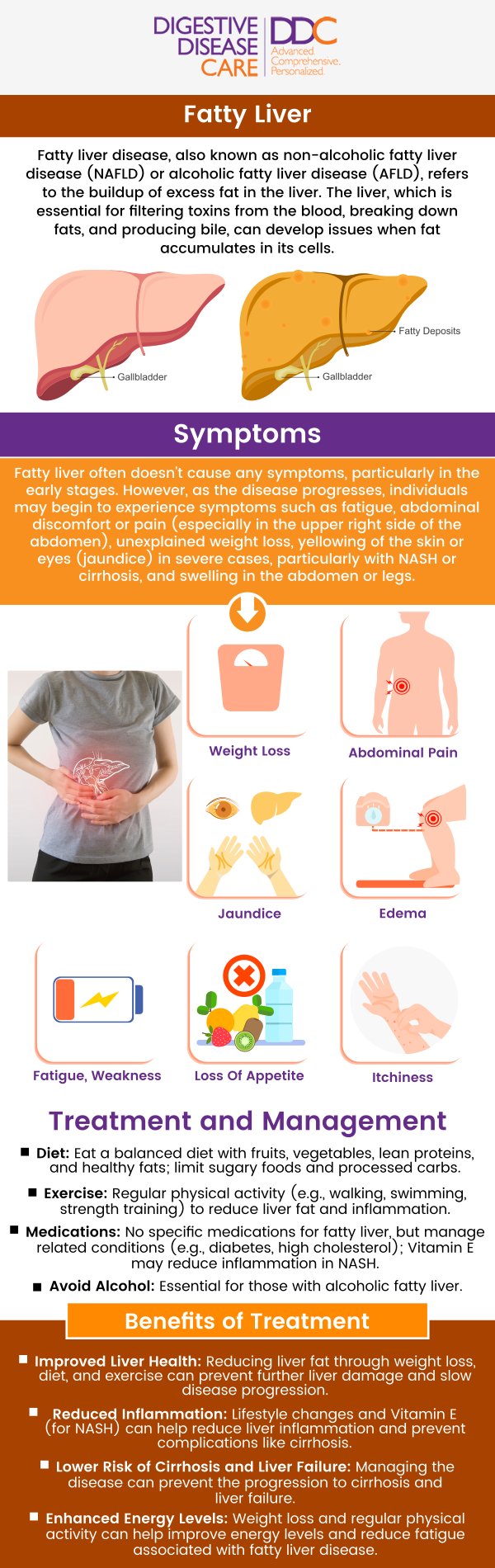
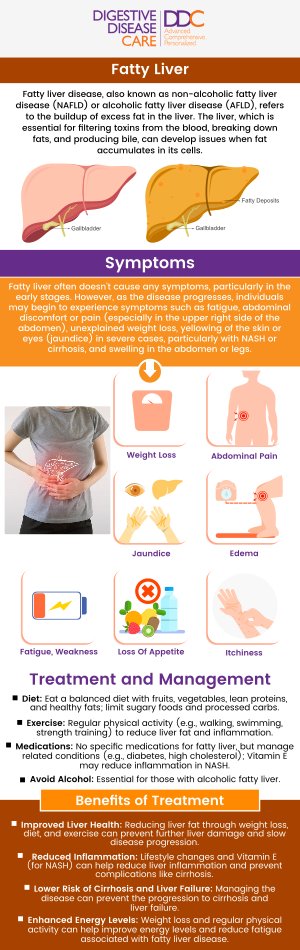
Table of Contents:
What is alcoholic liver disease?
What are the symptoms of alcoholic liver disease?
What are the stages of alcoholic liver disease?
How is alcoholic liver disease diagnosed?
Alcoholic liver disease is a serious condition that develops from long-term, excessive alcohol consumption, leading to progressive liver damage. The liver, which is responsible for processing nutrients and detoxifying harmful substances, becomes overwhelmed when exposed to chronic alcohol use. This process typically begins with fatty liver (steatosis), the earliest stage, where fat accumulates within liver cells. If alcohol use continues, the condition can progress to alcoholic hepatitis, marked by inflammation and symptoms such as jaundice, abdominal pain, nausea, and fever.
The most advanced stage is cirrhosis, which involves permanent scarring of the liver and severe impairment of its function. Cirrhosis increases the risk of liver failure, internal bleeding, and liver cancer. While not all heavy drinkers develop every stage, the likelihood rises with the duration and amount of alcohol consumption. Early detection, timely medical care, and complete alcohol cessation are key steps in preventing progression and preserving liver health.
Alcoholic liver disease is a progressive condition caused by long-term, excessive alcohol consumption, which damages the liver and interferes with its ability to function properly. Recognizing the symptoms is essential, as early intervention can slow or prevent the condition from advancing to more severe stages.
Key symptoms of alcoholic liver disease include:
• Fatigue and persistent weakness
• Loss of appetite and unintended weight loss
• Nausea and digestive discomfort
• Abdominal pain, especially in the upper right side
• Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
• Swelling in the abdomen (ascites) or legs (edema) from fluid buildup
• Easy bruising or bleeding due to reduced clotting function
• Confusion, memory issues, or personality changes caused by toxin buildup (hepatic encephalopathy)
Not everyone experiences symptoms in the early stages, which is why regular screening is important for those at risk. If you notice these warning signs, seeking a timely medical evaluation can help protect your liver health. Early diagnosis, alcohol cessation, and professional care play a vital role in managing alcoholic liver disease and preventing life-threatening complications.
Alcoholic liver disease progresses in stages, each reflecting increasing liver damage caused by chronic and excessive alcohol consumption. Recognizing these stages helps with early diagnosis and timely intervention, which can slow or even prevent further progression.
The three main stages of alcoholic liver disease include:
• Alcoholic Fatty Liver (Steatosis): Fat buildup in liver cells, often without symptoms. This stage is usually reversible if alcohol use is stopped.
• Alcoholic Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver with symptoms such as jaundice, abdominal pain, fever, and nausea. This stage requires prompt medical attention.
• Alcoholic Cirrhosis: Permanent scarring that significantly reduces liver function, leading to severe complications such as swelling, bleeding, confusion, and increased risk of liver cancer.
Not all individuals who drink heavily will experience every stage, but the risk increases with the duration and amount of alcohol consumed. Early detection, lifestyle changes, and medical care are essential in protecting liver function and preventing life-threatening outcomes.
Alcoholic liver disease is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory testing, and imaging studies. Since early stages may not cause noticeable symptoms, accurate evaluation is essential for timely intervention and prevention of further liver damage.
Key steps in diagnosing alcoholic liver disease include:
• Taking a detailed medical history, including alcohol consumption patterns, duration, and related symptoms.
• Performing a physical examination to check for signs such as jaundice, an enlarged or tender liver, and abdominal swelling (ascites).
• Ordering blood tests to measure liver enzymes (AST, ALT), bilirubin, albumin levels, and clotting function (prothrombin time).
• Using advanced imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI to assess liver structure, detect cirrhosis, or identify complications.
• Conducting a liver biopsy in select cases to provide a definitive diagnosis and measure the extent of scarring and inflammation.
• Ruling out other liver diseases such as viral hepatitis, autoimmune conditions, or metabolic disorders.
A thorough, step-by-step approach ensures an accurate diagnosis and helps guide the most effective treatment plan. Early detection at a specialized center improves outcomes and supports long-term liver health. For more information, contact us today or schedule an appointment online. We have convenient locations to serve you in Babylon NY, East Setauket NY, Forest Hills NY, Jericho NY, Lake Success NY, Melville NY, Mineola NY, Massapequa NY, New Hyde Park NY, and Riverhead NY and surrounding areas.

Check Out Our 5 Star Reviews


Additional Services You May Like

Additional Services You May Like
- Abdominal Pain
- Acid Reflux
- Barretts Esophagus
- Bloating
- Capsule Endoscopy
- Celiac Disease
- Colon Cancer Screening
- Colonoscopy
- Constipation
- Crohns Disease
- Diarrhea
- Diverticulitis
- Esophageal PH Monitoring
- Fatty Liver
- Fibroscan
- Gallstones
- Gastroenterologist
- Gastric Chest Pain
- Gluten Intolerance
- Hemorrhoid
- Hemorrhoid Banding
- Hepatitis
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Lactose Intolerance
- Pancreatitis
- Polyps
- Rectal Bleeding
- Stomach
- Ulcerative Colitis
- GI Urgent Care





