Celiac Disease vs. Gluten Sensitivity: What’s the Difference?
Celiac disease and gluten sensitivity both involve adverse reactions to gluten, but they differ in causes and long-term effects. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes intestinal damage, while gluten sensitivity leads to discomfort without causing lasting harm. At Digestive Disease Care, our gastroenterologists provide specialized diagnosis and treatment for both conditions to help manage symptoms and improve your quality of life. For more information, contact us today or schedule an appointment online. We have convenient locations to serve you in Babylon NY, East Setauket NY, Forest Hills NY, Jericho NY, Lake Success NY, Melville NY, Mineola NY, Massapequa NY, New Hyde Park NY, and Riverhead NY.
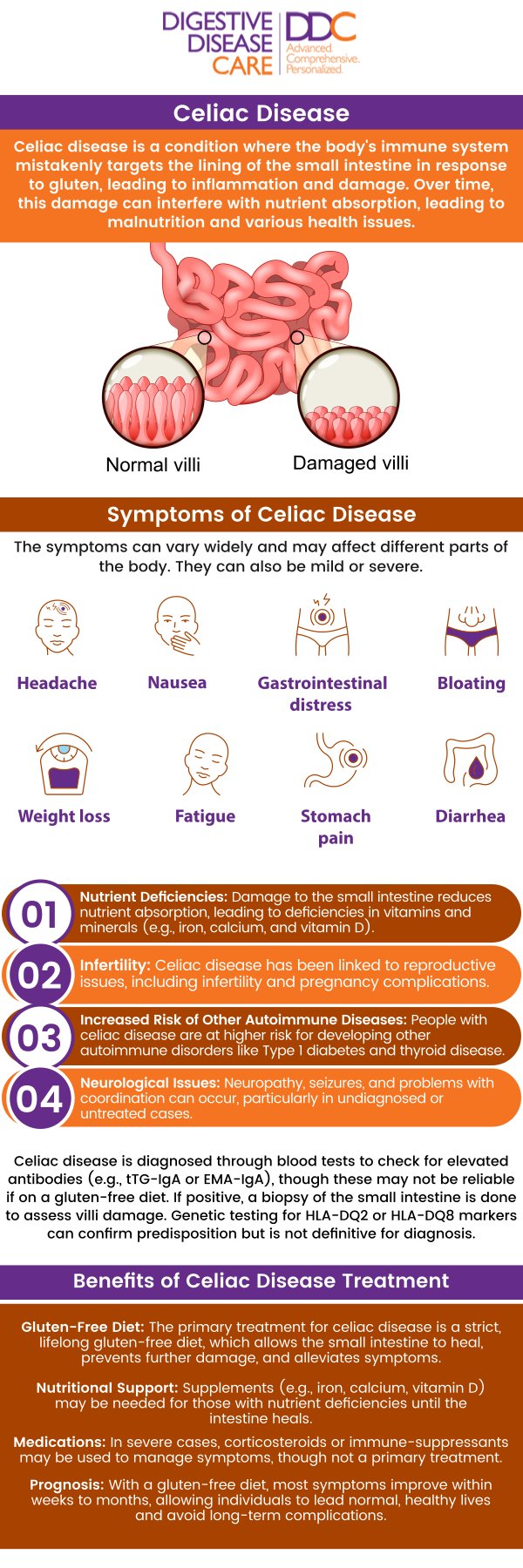
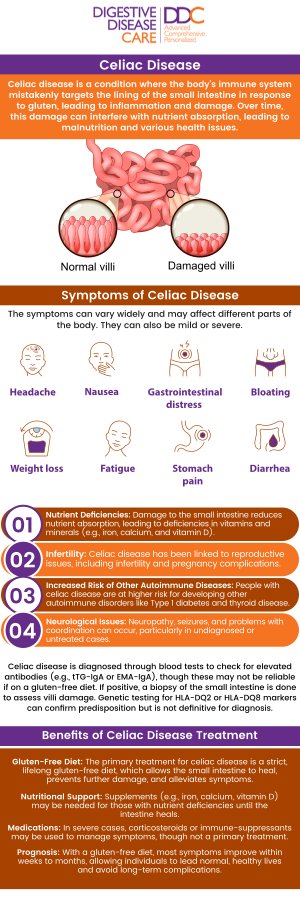
Table of Contents:
What is the difference between celiac disease and gluten sensitivity?
How do the symptoms of celiac disease differ from those of gluten sensitivity?
Can gluten sensitivity lead to long-term health problems like celiac disease?
Can you have both celiac disease and gluten sensitivity?
Celiac disease and gluten sensitivity are both conditions related to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. Although they share similar symptoms, such as abdominal discomfort and fatigue, they are distinct conditions with different underlying causes and health implications. Understanding the differences between the two is important for proper diagnosis and management, as the treatments and long-term effects vary. Below, we outline the key differences between celiac disease and gluten sensitivity.
Difference Between Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity:
1. Underlying Mechanism
• Celiac Disease: An autoimmune disorder where gluten triggers an immune response, causing damage to the small intestine.
• Gluten Sensitivity: Involves symptoms similar to celiac disease but without the autoimmune reaction or damage to the intestines.
2. Symptoms
• Celiac Disease: Common symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, fatigue, and nutrient deficiencies. It can also lead to more severe issues like osteoporosis or infertility if untreated.
• Gluten Sensitivity: Symptoms can include bloating, abdominal discomfort, fatigue, and headaches, but there’s no long-term damage to the intestine.
3. Diagnostic Methods
• Celiac Disease: Diagnosis is made through blood tests and a biopsy of the small intestine to assess damage.
• Gluten Sensitivity: There are no specific tests for gluten sensitivity. It is diagnosed by excluding other conditions like celiac disease or wheat allergies.
4. Health Consequences
• Celiac Disease: If left untreated, it can cause serious complications such as malnutrition, osteoporosis, and an increased risk of certain cancers.
• Gluten Sensitivity: While uncomfortable, gluten sensitivity doesn’t cause permanent damage to the intestines or other organs.
5. Treatment
• Celiac Disease: The only treatment is a strict, lifelong gluten-free diet.
• Gluten Sensitivity: Symptoms improve with a gluten-free diet, but it may not be as strictly necessary as for celiac disease.
The symptoms of celiac disease and gluten sensitivity can overlap, making it challenging to differentiate between the two. However, there are key differences in the nature of symptoms, their underlying causes, and long-term health implications.
Symptoms of Celiac Disease:
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder where consuming gluten triggers an immune response that damages the small intestine.
Common symptoms include:
1. Abdominal Pain and Bloating: These are common in celiac disease due to inflammation in the small intestine.
2. Diarrhea or Constipation: Disruptions in bowel habits are common as the intestines are unable to absorb nutrients properly.
3. Fatigue and Weight Loss: Chronic fatigue, along with unintentional weight loss, often occurs due to nutrient malabsorption.
4. Nutrient Deficiencies: As the intestines are damaged, vitamin and mineral deficiencies (e.g., iron, calcium, and vitamin D) are common.
5. Skin Conditions: Some individuals experience a rash called dermatitis herpetiformis, an itchy skin condition linked to gluten consumption.
Symptoms of Gluten Sensitivity:
Gluten sensitivity (non-celiac gluten sensitivity) involves symptoms similar to celiac disease but without the autoimmune reaction or damage to the intestines.
Key differences in symptoms include:
1. Abdominal Discomfort: People with gluten sensitivity may experience bloating and discomfort, but without the significant inflammation or damage seen in celiac disease.
2. No Nutrient Deficiencies: Unlike celiac disease, there is no damage to the intestines, so nutrient deficiencies are not typically present.
3. Fatigue and Headaches: Common symptoms, but without the long-term effects of malabsorption.
4. No Skin Conditions or Intestinal Damage: Gluten sensitivity does not cause dermatitis herpetiformis or damage to the small intestine, unlike celiac disease.
In conclusion, while the symptoms may be similar, the key difference is that celiac disease causes intestinal damage and long-term health risks, whereas gluten sensitivity does not.
Gluten sensitivity does not lead to long-term health problems in the same way that celiac disease can. Although both conditions involve adverse reactions to gluten, their mechanisms and long-term effects are very different.
Here’s a breakdown of the key points:
Differences Between Gluten Sensitivity and Celiac Disease:
1. No Intestinal Damage
• Gluten Sensitivity: Gluten sensitivity causes symptoms like abdominal discomfort and fatigue, but it does not damage the small intestine or cause inflammation.
• Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to attack and damage the lining of the small intestine, leading to inflammation and long-term complications.
2. Reversible Symptoms
• Gluten Sensitivity: Symptoms of gluten sensitivity, such as bloating or fatigue, typically resolve when gluten is removed from the diet. There are no lasting health issues once gluten is eliminated.
• Celiac Disease: If untreated, celiac disease can lead to malabsorption of nutrients, vitamin and mineral deficiencies, osteoporosis, infertility, and an increased risk of cancer.
3. No Risk of Complications
• Gluten Sensitivity: Gluten sensitivity does not lead to severe complications like small intestine damage, cancer, or autoimmune disorders.
• Celiac Disease: Untreated celiac disease can lead to serious complications such as osteoporosis, infertility, neurological issues, and gastrointestinal cancers.
4. Dietary Management
• Gluten Sensitivity: A gluten-free diet typically alleviates symptoms without causing any permanent damage.
• Celiac Disease: A strict, lifelong gluten-free diet is necessary to prevent ongoing damage and complications associated with celiac disease.
In conclusion, while both gluten sensitivity and celiac disease cause discomfort when gluten is consumed, gluten sensitivity does not lead to the same long-term health problems as celiac disease.
It is possible to have both celiac disease and gluten sensitivity, although this is rare. These conditions are distinct but can occur together in some individuals.
Below are the key points about the possibility of having both:
1. Celiac Disease and Its Autoimmune Nature
• Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder where gluten triggers the immune system to attack the small intestine, causing inflammation and potential long-term damage. It leads to symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue, and requires a strict, lifelong gluten-free diet to prevent further damage.
2. Gluten Sensitivity Is Non-Autoimmune
• Gluten sensitivity, or non-celiac gluten sensitivity, causes symptoms like bloating, fatigue, and abdominal discomfort without triggering an autoimmune response or causing damage to the intestines. It can be managed by eliminating gluten from the diet.
3. Possible Coexistence of Both Conditions
• Some individuals may experience both celiac disease and gluten sensitivity, meaning they have the autoimmune damage of celiac disease and also suffer from lingering gluten-related symptoms despite following a gluten-free diet.
4. Complicated Diagnosis
• Diagnosing both conditions can be challenging because the symptoms of gluten sensitivity can overlap with those of celiac disease. Blood tests and biopsies are used to confirm celiac disease, but gluten sensitivity is typically diagnosed by exclusion.
5. Management of Both Conditions
• Managing both requires a strict gluten-free diet to treat celiac disease and additional strategies, such as symptom management and dietary adjustments, to address gluten sensitivity.
If both conditions are suspected, it is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan for both celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. For more information, contact us today or schedule an appointment online. We have convenient locations to serve you in Melville NY, New Hyde Park NY, Forest Hills NY, Jericho NY, Mineola NY, Lake Success NY, Babylon NY, East Setauket NY, Massapequa NY, Riverhead NY and BEYOND.

Check Out Our 5 Star Reviews


Additional Services You May Like

Additional Services You May Like
- Abdominal Pain
- Acid Reflux
- Barretts Esophagus
- Bloating
- Capsule Endoscopy
- Celiac Disease
- Colon Cancer Screening
- Colonoscopy
- Constipation
- Crohns Disease
- Diarrhea
- Diverticulitis
- Esophageal PH Monitoring
- Fatty Liver
- Fibroscan
- Gallstones
- Gastroenterologist
- Gastric Chest Pain
- Gluten Intolerance
- Hemorrhoid
- Hemorrhoid Banding
- Hepatitis
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Lactose Intolerance
- Pancreatitis
- Polyps
- Rectal Bleeding
- Stomach
- Ulcerative Colitis
- GI Urgent Care





