Upper Abdominal Pain After Eating: What It Could Mean
Upper abdominal pain after eating can be caused by various digestive issues, including indigestion, acid reflux, or gallstones. Conditions like gastritis or peptic ulcers can also trigger discomfort, especially after consuming rich or fatty foods. If the pain is persistent or severe, it could indicate a more serious underlying condition, like a gallbladder issue or liver dysfunction. Seeking medical advice from a healthcare professional, Dr. Preeti Mehta, MD, and our team of board-certified gastroenterologists at Digestive Disease Care can help identify the cause and provide appropriate treatment. For more information, contact us today or schedule an appointment online. We have convenient locations to serve you in Babylon NY, East Setauket NY, Forest Hills NY, Jericho NY, Lake Success NY, Melville NY, Mineola NY, Massapequa NY, New Hyde Park NY, and Riverhead NY.
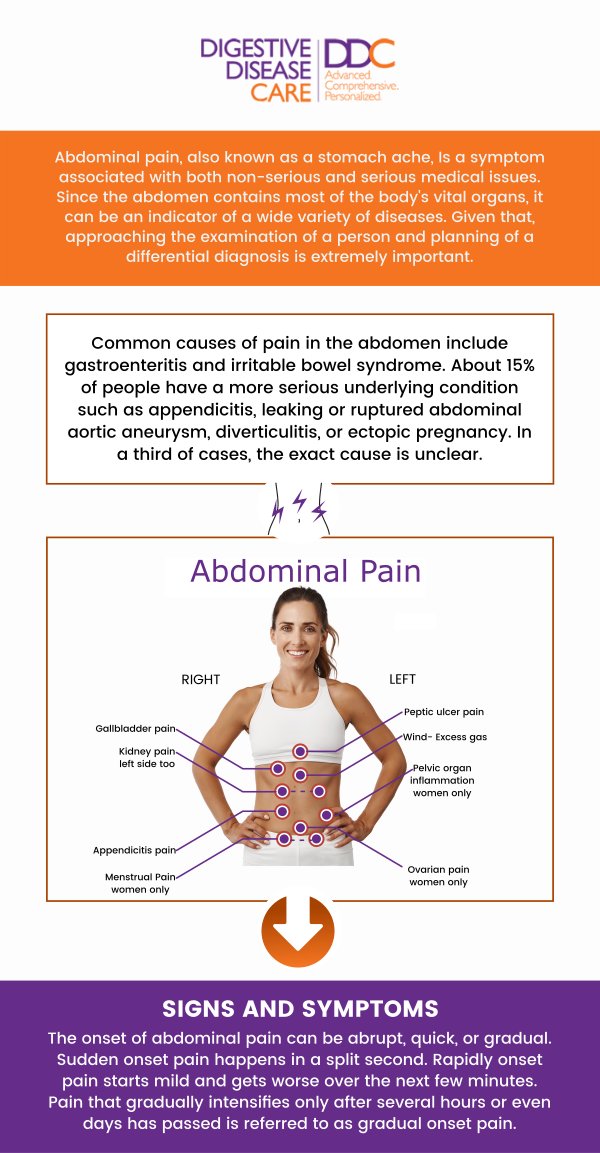
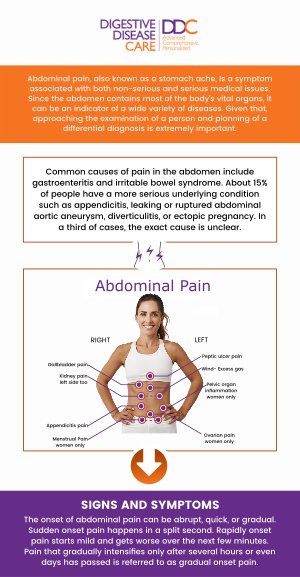
Table of Contents:
What causes upper abdominal pain after eating?
How can indigestion lead to upper abdominal pain after eating?
Is upper abdominal pain after eating a sign of acid reflux?
Can gallstones cause upper abdominal pain after meals?
Dr. Preeti Mehta, MD at Digestive Disease Care: Causes of Upper Abdominal Pain After Eating and How to Find Relief
Upper abdominal pain after eating can be caused by a variety of conditions, ranging from indigestion to more serious digestive issues. Here are some common causes:
• Indigestion (Dyspepsia): One of the most frequent causes of upper abdominal pain after eating is indigestion, often resulting from overeating, eating too quickly, or consuming fatty, spicy, or acidic foods. This discomfort may also be accompanied by bloating, nausea, or burping.
• Gastritis: Gastritis is the inflammation of the stomach lining, often caused by excessive alcohol consumption, certain medications (like NSAIDs), or a bacterial infection (Helicobacter pylori). The pain from gastritis tends to worsen after eating and may be relieved by antacids or food.
• Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): GERD occurs when stomach acid leaks into the esophagus, causing heartburn and pain in the upper abdomen, particularly after meals. Spicy foods, caffeine, or alcohol can trigger or worsen GERD symptoms.
• Peptic Ulcers: Ulcers in the stomach or the upper part of the small intestine can cause sharp or burning pain after eating. This pain may worsen on an empty stomach or after consuming acidic foods.
• Gallstones: Gallstones can block the bile ducts and cause severe pain in the upper abdomen, especially after eating fatty foods. This pain may also radiate to the back or right shoulder.
• Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas can result in severe upper abdominal pain after eating, particularly if the pain is associated with fatty meals. This condition often requires immediate medical attention.
• Food Intolerances or Allergies: Some individuals may experience abdominal pain after eating certain foods, such as dairy, gluten, or high-fiber foods, due to food intolerances or allergies.
If you experience persistent or severe upper abdominal pain after eating, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia, is a common cause of upper abdominal pain after eating. It occurs when the digestive system experiences difficulty in breaking down food, leading to discomfort and bloating. Here’s how indigestion can cause pain in the upper abdomen after eating:
• Slowed Digestion: When food moves too slowly through the stomach and intestines, it can cause a feeling of fullness and discomfort in the upper abdomen. This delayed digestion is often a result of overeating, eating large meals, or consuming heavy, fatty foods that are harder to digest.
• Acid Reflux: Indigestion can also lead to acid reflux, where stomach acid travels up into the esophagus. This can result in a burning sensation and pain in the upper abdominal area. The pain often worsens after eating, especially after consuming spicy, fatty, or acidic foods.
• Increased Gas Production: As food is broken down in the stomach and intestines, gas is produced. In cases of indigestion, excess gas can accumulate in the stomach, causing bloating and discomfort in the upper abdomen. This bloating can lead to pain after eating, especially if the stomach is already full or contains large amounts of food.
• Stomach Acid Imbalance: Indigestion can occur when there is an imbalance in stomach acid production. Too much acid can irritate the stomach lining, while too little acid can hinder digestion. Both conditions can lead to discomfort in the upper abdomen, particularly after eating, when the digestive system is actively working to process food.
• Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress and anxiety can also contribute to indigestion. Stress can increase stomach acid production, affect digestion, and lead to muscle tension in the abdomen, causing discomfort and pain after meals.
Indigestion is often triggered by lifestyle factors such as poor eating habits, stress, or certain foods. If you experience persistent upper abdominal pain after eating, it is important to address the underlying cause and seek medical advice for proper management.
Upper abdominal pain after eating can indeed be a sign of acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid or bile irritates the lining of the esophagus, leading to discomfort. Here’s how acid reflux can cause upper abdominal pain after eating:
• Acid Backflow: After eating, food enters the stomach, where it is mixed with stomach acid for digestion. In individuals with acid reflux, the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a valve between the stomach and esophagus, does not close properly. This causes stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, which can result in pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen, often felt as a burning sensation.
• Heartburn and Discomfort: One of the hallmark symptoms of acid reflux is heartburn, a burning feeling in the chest or upper abdomen. This sensation often worsens after eating, especially after consuming fatty, spicy, or acidic foods. The pain can radiate from the stomach to the chest, sometimes mimicking a heart attack.
• Bloating and Gas: Acid reflux can also cause bloating and gas after eating, especially when large or rich meals are consumed. This bloating can add pressure to the upper abdomen, intensifying discomfort.
• Regurgitation of Food or Acid: In some cases, acid reflux may cause food or acid to regurgitate back into the mouth. This is often accompanied by a sour or bitter taste and can contribute to upper abdominal pain, as the stomach acid irritates the esophagus and stomach lining.
• Worsened by Eating Habits: Certain foods and beverages, such as citrus, coffee, alcohol, chocolate, or fried foods, can trigger or worsen acid reflux symptoms. Eating large meals or lying down soon after eating can also exacerbate the discomfort.
If you experience persistent upper abdominal pain after eating, especially along with heartburn or regurgitation, it may be a sign of acid reflux or GERD. Consulting a healthcare provider is important to receive a proper diagnosis and treatment, as untreated acid reflux can lead to more serious complications.
Yes, gallstones can cause upper abdominal pain after meals, particularly after eating fatty foods. Gallstones are solid particles that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver, which stores bile that helps digest fats. When gallstones block the bile ducts or disrupt the flow of bile, it can lead to intense discomfort, especially after eating. Here’s how gallstones can cause upper abdominal pain after meals:
• Bile Blockage: When gallstones obstruct the bile ducts, the bile produced by the liver is unable to flow into the small intestine as it should. This blockage can cause bile to build up, leading to intense pain, typically felt in the upper right side of the abdomen. This pain often occurs after eating, especially after consuming fatty foods that stimulate bile production.
• Pain from Gallbladder Contraction: After eating, the body signals the gallbladder to release bile to aid in digestion. If a gallstone blocks the bile duct, the gallbladder contracts forcefully in an attempt to release the bile, causing sharp, cramp-like pain. This pain is often sudden and intense, lasting from minutes to hours.
• Fatty Food Triggers: Fatty foods stimulate the gallbladder to release bile, which can trigger pain in people with gallstones. Foods high in fat, such as fried foods, cheese, and red meat, are more likely to provoke gallstone-related pain because they require more bile for digestion.
• Dyspepsia (Indigestion): In some cases, gallstones can cause indigestion or dyspepsia, resulting in bloating, nausea, and discomfort in the upper abdomen after meals. This can be mistaken for other digestive issues but is often linked to gallbladder dysfunction caused by gallstones.
• Biliary Colic: This term refers to the sharp, cramp-like pain that occurs when a gallstone temporarily blocks a bile duct. The pain typically occurs after meals, particularly large or fatty ones, and is usually concentrated in the upper abdomen or upper right side of the body. It can last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours.
If you experience persistent upper abdominal pain after eating, particularly after consuming fatty foods, it could be a sign of gallstones. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment, as untreated gallstones can lead to more serious complications like infection or inflammation of the gallbladder.
If you’re experiencing upper abdominal pain after eating, Dr. Preeti Mehta, MD, at Digestive Disease Care, can help identify the underlying causes and provide effective treatment options. Upper abdominal pain after meals can be caused by various conditions such as indigestion, acid reflux, gallstones, or gastritis. Dr. Mehta and her team of board-certified gastroenterologists offer comprehensive care to diagnose and manage these conditions. With a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan, they aim to provide relief from discomfort and improve your digestive health.
At Digestive Disease Care, we understand how disruptive upper abdominal pain can be to your daily life. Whether your symptoms are related to digestive issues like GERD, bloating, or gallbladder problems, Dr. Preeti Mehta, MD, and her team are committed to offering accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment options. For more information, contact us today or schedule an appointment online. We have convenient locations to serve you in Babylon NY, East Setauket NY, Forest Hills NY, Jericho NY, Lake Success NY, Melville NY, Mineola NY, Massapequa NY, New Hyde Park NY, and Riverhead NY.

Check Out Our 5 Star Reviews


Additional Services You May Like

Additional Services You May Like
- Abdominal Pain
- Acid Reflux
- Barretts Esophagus
- Bloating
- Capsule Endoscopy
- Celiac Disease
- Colon Cancer Screening
- Colonoscopy
- Constipation
- Crohns Disease
- Diarrhea
- Diverticulitis
- Esophageal PH Monitoring
- Fatty Liver
- Fibroscan
- Gallstones
- Gastroenterologist
- Gastric Chest Pain
- Gluten Intolerance
- Hemorrhoid
- Hemorrhoid Banding
- Hepatitis
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Lactose Intolerance
- Pancreatitis
- Polyps
- Rectal Bleeding
- Stomach
- Ulcerative Colitis
- GI Urgent Care





